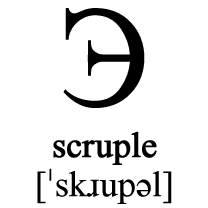What do elephants and camels have in common?
Well, words for camel in Slavic languages like Czech and Russian possibly come from an Ancient Greek word meaning elephant.
In Czech the word for camel is velbloud [ˈvɛlblou̯t], which comes from the Proto-Slavic *velьb(l)ǫdъ / vъlьb(l)ǫdъ (camel), from the Gothic 𐌿𐌻𐌱𐌰𐌽𐌳𐌿𐍃 (ulbandus – camel), from the Latin elephantus (elephant), from the Ancient Greek ἐλέφας (eléphas – elephant) [source].
Words from camel in other Slavic languages come from the same root: верблюд (verbljúd) in Russian and Ukrainian, вярблюд (vjarbljúd) in Belarusian, wielbłąd in Polish, and so on [source].
These all come from the Gothic 𐌿𐌻𐌱𐌰𐌽𐌳𐌿𐍃 (ulbandus), but from there the etmological trial gets a bit hazy, as they quite often do. Traditionally this word is thought to derive from the Greek ἐλέφας, via the Latin elephantus.
Another theory is that the Gothic word comes from the Proto-Germanic *elpanduz (elephant, camel), which possibly comes from the Hittite word hu(wa)lpant (humpback), or from another ancient language of Anatolian such as Luwian [source].
The word for elephant in Czech (and also in Slovak, Serbian, Croatian and Slovenian) is slon [slon], which comes from the Proto-Slavic *slonъ (elephant) [source], which comes either from the Turkish aslan (lion), or from *sloniti (to lean against), relating to the medieval story of an elephant sleeping leaning on a tree [source].
So now we know where the name of the lion in The Lion, The Witch and The Wardrobe probably comes from.