
Here’s a recording in a mystery language.
Do you know or can you guess the language, and do you know where it’s spoken?

Here’s a recording in a mystery language.
Do you know or can you guess the language, and do you know where it’s spoken?
The English word ruche [ɹuʃ] means a gathered ruffle or pleat of fabric used for trimming or decorating garments [source], or to flute, pleat or bunch up (fabric) [source].
It comes from the French word ruche [ʁyʃ], which means a (bee)hive, ruffle or flounce, and comes from the Middle French rusche (beehive), from the Medieval Latin rusca (bark), from the Gaulish *ruskā, from the Proto-Celtic *rūskos (bark, beehive) [source], from the Proto-Indo-European h₃rewk- (to dig (up), till) [source].
Words from the same Proto-Celtic root include:
Sources: Grand Terrier Edition Skol Vreizh, TERMOFIS, catalandictionary.org, gerlyver kernewek, ReversoDictionary, teanglann.ie, On-Line Manx Dictionary, Bokmålsordboka | Nynorskordboka, Am Faclair Beag, Svenska Akademiens Ordböcker, Geiriadur Prifysgol Cymru
What do the words care and garrulous have in common?
Well, care comes from the Middle English care (grief, sorrow), from the Old English caru/ċearu (worry, anxiety, care, sorrow, grief), from the Proto-West-Germanic *karu (care, worry), from the Proto-Germanic *karō (complaint, lament, grievance, moan, worry, sorrow, care, concern), from the Proto-Indo-European *ǵeh₂r- (to shout, call, cry; voice) [source].
Garrulous (excessively or tiresomely talkative) comes from the Latin garrulus (talkative), from garriō (I chatter, prattle), from the Proto-Indo-European *ǵeh₂r- (to call, cry), which is apparently of imitative origin [source].
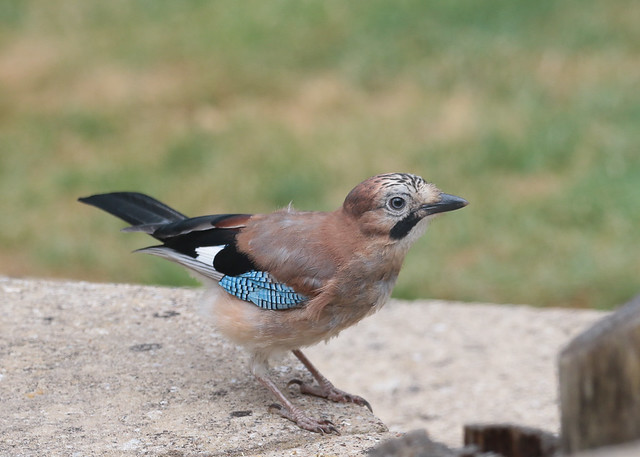

Pictured above is a Eurasian Jay, also known as Garrulus glandarius – the garrulus part means chattering/noisy and the glandarius part means “of acorns”.
So, they come from the same PIE root, via different paths. Other words from the same root include [source]:
The English word slogan also comes from the same root, or at least part of it does. It comes from sloggorne/slughorn(e) (battle cry), from the Scottish Gaelic sluagh-ghairm [ˈsl̪ˠuəɣərəm] (slogan, war cry), from the Old Irish slúag/slóg (army, assembly, crowd) and gairm (call, cry).

Here’s a recording in a mystery language.
Do you know or can you guess the language, and do you know where it’s spoken?
The Scots word fecht [fɛçt / feːçt / faeçt] means to fight, or to struggle in the battle of life against misfortune, poverty, etc. It comes from the Middle English fighten (to fight, battle, quarrel), from the Old English feohtan (to fight), from the Proto-West Germanic *fehtan (to fight), from the Proto-Germanic *fehtaną (to comb, detangle, struggle (with), fight, shear) from the Proto-Indo-European *peḱ- (to pluck, ruffle, tousle, shear) [source].
Related words include:
Source: DSL Dictionaries of the Scots Language / Dictionars o the Scots Leid
I learnt about this word on a video on Tiktok by @misspunnypennie – part of her Scots word of the day series. This particular video is about the word ilka, which means each or every. The example she gives includes fecht and fechter:
Agin ilka sair fecht there’s a bonnie fechter
(Against every hard fight there’s a fearless fighter)
By the way, if you prefer to avoid Tiktok, you can find compilations of the Scots Word of Day videos, and Scots-related videos by Miss Punny Pennie (a.k.a. Len Pennie) on Twitter and YouTube. Here’s Len talking about Scots:
When I heard the words fecht and fechter, I thought they must be related to the Dutch words vechten [ˈvɛxtə(n] (to fight, fighting) and vechter (fighter, warrior), which I learnt recently – they are indeed related and come from the same Proto-West-Germanic root [source].
Other words from the same Proto-West-Germanic root (*fehtan) include: fight in English, fäkta (to fence, fight) in Swedish, fechten (to fence, fight) in German, and фехтовать [fʲɪxtɐˈvatʲ] (to fence) in Russian, which was borrowed from German. To fence here means to fight with swords rather than to make a fence [source]
There is also a Dutch word related to ilka – elk, which means each or every [source].

Here’s a recording in a mystery language.
Do you know or can you guess the language, and do you know where it’s spoken?
The Irish word ceolchoirm [ˈcʲolˠ.xorʲəmʲ] means concert. It is made up of ceol (music) and coirm [korʲəmʲ] (feast, banquet, ale, beer). There are similar words in Scottish Gaelic (cuirm-chiùil), and Manx (cuirrey kiaull) [source].
The word coirm comes from the Old Irish word coirm (ale, beer), from the Proto-Celtic *kurmi (beer). Words for beer in the Brythonic Celtic languages come from the same root: cwrw in Welsh, and korev in Cornish and Breton [source].
The Latin word cervēs(i)a [kerˈu̯eː.si.a], which means beer made of wheat, especially of higher quality, comes from the same Proto-Celtic root, as do words for beer in some Romance languages, including cervexa in Galician, cervesa in Catalan and Occitan, cerveza in Spanish and cerveja in Portuguese [source].
From the same Proto-Celtic root we get the French word cervoise [sɛʁ.vwaz], which was a kind of ale or beer made from barley or wheat and without hops during the Middle Ages [source]. The archaic Italian word cervogia [t͡ʃerˈvɔ.d͡ʒa] (beer, ale made from barley or oats) was borrowed from the Old French cervoise [source].
The usual French word for beer is bière [bjɛʁ], which was borrowed from the Middle Dutch bier/bēr (beer), from the Old Dutch *bier, from Frankish *bior (beer), from the Proto-Germanic *beuzą (beer) [source].
Words for beer is some Germanic languages come from the same root, including Bier in German, bier in Dutch, and beer in English [source].
The Italian word for beer, birra, was borrowed from the German Bier, and the Greek word μπίρα (bíra – beer, ale) was borrowed from Italian, as were words for beer in Arabic, بِيرَا (bīrā), Maltese, birra, and Turkish, bira [source].
The Irish word beoir (beer) comes from the Middle Irish beóir (beer), from Old Norse bjórr (beer), which also has descendents in Scottish Gaelic (beòir), Manx (beer), Icelandic (bjór) and Faroese (bjór) [source].
Another word for beer or ale in North Germanic languages is øl (in Danish, Faroese, Norwegian) / öl (in Swedish and Icelandic). This comes from the Old Norse word ǫl (ale, beer), possibly from the Proto-Norse ᚨᛚᚢ (alu – ale), from the Proto-Germanic *alu (beer, ale), from Proto-Indo-European *h₂elut- (beer) [source].
Words for beer in Finnic languages possibly come from the same Proto-Germanic root, including õlu in Estonian, olut in Finnish, Igrian, Karelian and Veps, and oluq in Võro [source].
In Slavic languages words for beer come from the Proto-Slavic *pȋvo (drink, beer, beverage), including пиво (pivo) in Russian, Rusyn, Ukrainian, Bulgarian, Macedonian and Serbian, pivo in Slovenian, Czech and Slovak, and piwo in Polish and Sorbian [source].
Here’s a map of words for beer in European languages:
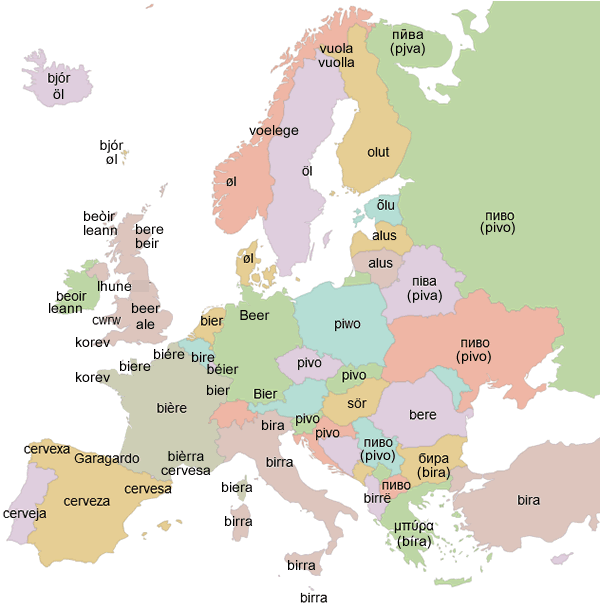
Source: https://ukdataexplorer.com/european-translator/?word=beer
A Japanese lesson that I studied on Duolingo today included names of parts of Tokyo. One of these was 渋谷 (Shibuya), which, according to Wikipedia, is a major commercial and finance centre, and houses two of the busiest railway stations in the world, Shibuya (渋谷駅) and Shinjuku (新宿駅).
The first character in Shibuya (渋) is rare, and I haven’t seen it anywhere else. On it’s own it means the “astringent taste of unripe persimmon fruit” and is a simplified form of 澁 (jū/shibu), which is mainly used in personal names [source].
The second character in Shibuya (谷) means valley, lowland or plain. It’s pronounced tani, kiwa, koku or ya.
渋 is pronounced shū, sō, jū or shibu. It appears in words such as:
The character 澁 (sè) exists in Chinese, and is an old variant of 澀 [涩] (sè), which means astringent, tart, puckery,acerbity, unsmooth, rough, hard to understand, obscure. This is quite appropriate as it’s quite an obscure character.
Now trying saying 这柿子涩 (zhè shìzi sè) many times as quickly as you can. It means the persimmon tasts puckery, a word I hadn’t come across before that means high in tannins (of wine), causing pucking or tending to pucker.
Sources: jisho, MDBG, LINE Dict Chinese-English, The Free Dictionary

Here’s a recording in a mystery language.
Do you know or can you guess the language, and do you know where it’s spoken?
In the French conversation group last night, one of the members mentioned that she has been on the wagon for two weeks, or in other words, she has stopped drinking alcohol. French equivalents of being on the wagon include:
If you fall of the wagon (go back to drinking), then you could say:
In English, the expression to be on the wagon usually means
“abstaining from drinking any alcoholic drink, usually in the sense of having given it up (as opposed to never having partaken); teetotal”
It can also means “Maintaining a program of self-improvement or abstinence from some other undesirable habit.” (such as smoking).
It was apparently coined in the USA and was originally ‘on the water-cart’, and became ‘on the water-wagon’ the ‘on the wagon’. It referred to carts (like the one pictured above) that were used to hose down dusty roads. The idea was that someone who was ‘on the wagon’ was drinking water rather than alcoholic drinks.
It was possibly first used by the temperance movement, which emerged in the 19th century in organisations such as the Washingtonian movement (founded in 1840), The Woman’s Christian Temperance Union (founded in 1874) and The Anti-Saloon League (founded in 1893).
Sources: ReversoDictionary, Wiktionary, The Phrase Finder, Wikipedia
I have been on the wagon (teetotal) since 2002, and didn’t drink much alcohol before then anyway.
How do you talk about being ‘on the wagon’ or ‘falling off the wagon’ in other languages?