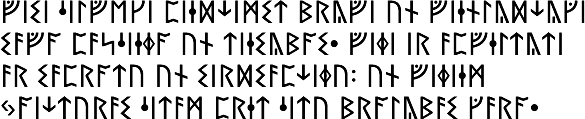Podcast: Play in new window | Download
Here’s the latest news from the world of Omniglot.
There are new language pages about:
- Burarra (Gu-jingarliya), an Arnhem language spoken in Arnhem Land in the Northern Territory of Australia.
- Limbum, an Eastern Grassfields language spoken mainly in Cameroon, and also in Nigeria
- Yankunytjatjara, a Pama-Nyungan language spoken in South Australia.
There are new numbers pages in:
- Maldivian / Dhivehi (ދިވެހި), an Indo-Aryan language spoken mainly in the Maldives.
- Venetian (vèneto), a Romance language spoken mainly in Venice and surrounding areas of Italy.
- Dagbani (Dagbanli), a Gur language spoken mainly in northern Ghana.
On the Omniglot blog there’s a new post entitled Cave Paintings Deciphered?, about recent news of the possible decoding of certain symbols found in cave paintings, and there’s the usual Language Quiz. See if you can guess what language this is:
Here’s a clue: this is language is spoken in China, but isn’t Mandarin
The mystery language in this week’s language quiz was Wendat (Waⁿdat), an Iroquoian language formerly spoken in parts of Oklahoma in the USA and Quebec in Canada which is being revived.
In this week’s Adventure in Etymology we’re Harbouring Harbingers, and finding out what links the words harbinger and harbour.
On the Celtiadur blog there’s a post about words for Halves and Sides and related things in Celtic languages.
I forgot to mention on the recording, but there’s also a new Celtic Pathways podcast about the words New & Year in Celtic languages.
For more Omniglot News see:
https://www.omniglot.com/news/
https://twitter.com/Omniglossia
https://www.facebook.com/groups/omniglot/
https://www.facebook.com/Omniglot-100430558332117
You can also listen to this podcast on: Apple Podcasts, Amazon Music, Stitcher, TuneIn, Podchaser, PlayerFM or podtail.
If you would like to support this podcast, you can make a donation via PayPal or Patreon, or contribute to Omniglot in other ways.