Podcast: Play in new window | Download
Today we’re exploring the origins of the word deck.
deck [dɛk] means:
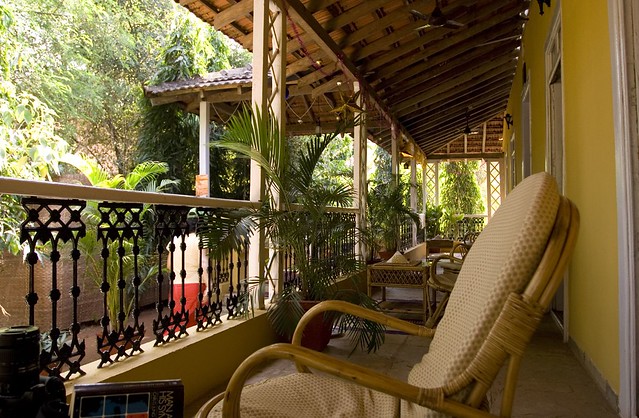
- Any raised flat surface that can be walked on: a balcony; a porch; a raised patio; a flat rooftop.
- The floorlike covering of the horizontal sections, or compartments, of a ship.
- A main aeroplane surface.
It comes from the Middle English dekke (the roof over any part of a boat or ship), from Middle Dutch dec (roof, covering), from decken (to roof, cover, protect), from Old Dutch thecken (to cover, roof), from Proto-West-Germanic *þakkjan (to cover), from Proto-Germanic *þakjaną [ˈθɑk.jɑ.nɑ̃] (to cover), *þaką (roof, cover), from PIE *(s)teg- (cover) [source].
Words from the same Proto-Germanic root (*þaką) include: thatch in English, dak (roof) and dekken [ˈdɛkə(n)] (to cover, set) in Dutch, Dach (roof) and decken (to cover, set) in German, tak (roof, ceiling) and täcka [tɛka] (to cover) in Swedish, and tag (roof) and tække (to thatch) in Danish [source].
Words from the same PIE root (*(s)teg-) include: detect, protect, tile and toga in English, tŷ (house) in Welsh, and teach (house) in Irish [source].
Here’s a video I made of this information:
Video made with Doodly [afflilate link].
I also write about words, etymology, and other language-related topics, on the Omniglot Blog, and I explore etymological connections between Celtic languages on the Celtiadur.
You can also listen to this podcast on: Apple Podcasts, Amazon Music, Stitcher, TuneIn, Podchaser, PlayerFM or podtail.
If you would like to support this podcast, you can make a donation via PayPal or Patreon, or contribute to Omniglot in other ways.