Karamojong is a member of the Eastern Nilotic branch of the Nilo-Saharan language family. It is spoken by at about 691,000 people in Karamoja in northeastern Uganda. The people speak it are call themselves ŋiKarimojoŋ / ŋiKaramojoŋ, which means something like "the old men sat down". It dates from about 300 years ago during a time of migration when this group refused to travel further on to what is now Teso.
Closely related languages and dialects are spoken by the Jie, ŋiDodos, iTeso people in Uganda, ŋiTurkana, iTesyo (Kenya), Jiye, ŋiToposa, (southern Sudan), and also by at least one tribe in Ethiopia. These peoples are part of the "Karimojong Cluster" of Nilotic tribes, which is known by some as the Teso Cluster.
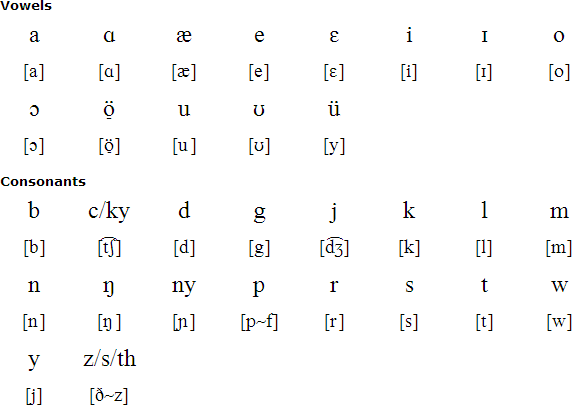
Download an alphabet chart for Karamojong (Excel)
Karamojong is a verb-initial language. Verb forms differ in aspect rather than tense; first person plural personal and possessive pronouns has inclusive and exclusive forms. Nouns and pronouns have gender prefixes, which can change meaning, eg ekitoi (m) means tree or medicine obtained from a tree / bush, akitoi (f) means log or firewood, and ikitoi (n) means twigs used for lighting cooking fires. The neuter often implies a diminutive – edia means boy and idia means little boy. There are no articles.
Pronunciation is phonetic (similar to Spanish), except as otherwise noted. There are no letters "F", "H" "Q", "X" or "Z" (but see next paragraph). "Ŋ" (or "ng" – as in "singing") and "Ny" are consonants in their own right. Sometimes "P" sounds more like "F” in English (so, when learning English, ŋaKarimojoŋ speakers sometimes confuse these sounds). "L" and "R" are NOT confused. There is tendency to mouthe a silent "O" or "U" on the end of some words ending with consonants. Adjacent vowels are usually pronounced without diphthongs.
The Roman alphabet is used, orthography rules were established by Missionaries in the 1960s. These rules varied slightly between the mainly British Anglicans and the mainly Italian Roman Catholics (RC). The most obvious example of this is the sound which is halfway between an "S" as in "sausage" and" th" as in "think". This was tendered by the Anglicans as "th" and the RCs as "Z". These days both "S "and "th" are used.
Rules also varied also between different people writing down different languages. For example, most Nilotic languages in and around Uganda spell the sound 'ch' as in church "c", whereas in the Bantu languages, at least in Uganda (and excluding kiSwahili), this sound is spelled "ky" (as in Burmese).
There is some confusion between the use of "I" and "Y" where there is a vowel following. General tendency is to assume that the "Y" sound comes from the conjunction of the vowels rather than being a separate letter, but not exclusively. But sometimes there are very similar words with different meanings: edia means boy, edya however means vegetables and any difference in pronunciation has little to do with the "y". Somewhat differently, akimat means old woman, or, to drink. If you say acamit ayoŋ akimat you are saying you want the old woman rather than you want to drink, so in this case the infinitive is rather oddly replaced by the vocative, thus acamit ayoŋ tomat to avoid confusion when you need a drink.
Almost all plural nouns are pre-fixed with ŋa (f) or ŋi (m & n). Special uses of these can be seen above for the language and people. There are generally suffixes on plural nouns which, to the learner at least, have little regularity, for example emong / ŋimongin – ox / oxen and akai / ŋakais - house/s, or even removal of last letter, thus emoru / ŋimor – mountain/s and aberu / ŋaber(u) – woman / women.
Most traditionally known liquids such as water, ŋakipi, and milk, ŋakile, are feminine plural (though the eng prefix has been lost in some dialects) whereas more recently introduced liquids such as (bottled) beer – ebiya are masculine singular. Male names mostly begin with "Lo" whilst female names begin with "Na", thus Lokiru and Nakiru are a boy and a girl born at the time of rain. In other Nilotic languages in the region, this rule applies without the "L" and "N".
Ejoka? - Hello! [literally "Is it good?"]
Ejok-nooi - Hello! [response]
alakara (nooi) - Thank you (very much) [literally "I am (very) happy"]
Ie-ia? (papa/toto/ikoku)? - How are you (father/mother/child)?
Ikianyun! - See you! (as "good-bye")
Ngai ekonikiro? - What is your name?
Ee - Yes
Mam! - No!
Akuj - God (apparently feminine - also means "north" and "up")
Ŋakipi - Water
Akim - Fire
Akine - Goat
emoŋin - Ox
emusugut (m sing), amusugut (f sing) - White person
Ai ilothi iyoŋ? or ai ilosi iyong? - Where are you going?
The main books written in the language are the New Testament, published in significantly different Anglican and RC versions in the 1960s, and a joint one published in the early 1990s. More recently there have been some educational books and there are various grammars and dictionaries produced mainly by RCs. The Old Testament is in process with a number of books already completed.
Information compiled by Nick Jewitt, who has worked with the Karamojong and speaks some of their language.
Information about the Karamojong language and people
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Karimojong
https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Karamojong_(langue)
http://wals.info/languoid/lect/wals_code_kmj
http://www.everyculture.com/Africa-Middle-East/Karamojong.html
http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/312137/Karimojong
http://www.karamoja.com/karimojong.html
Acholi, Adhola, Alur, Anuak, Ateso, Bari, Belanda Bor, Datooga, Dholuo, Dinka, Dongotono, Kakwa, Karamojong, Keiyo, Kipsigis, Kuku, Kupsabiny, Lango (South Sudan), Lango (Uganda), Lopit, Lotuko, Maasai, Mandari, Markwet, Nandi, Nuer, Nyangatom, Nyepu, Terik, Toposa, Tugen, Turkana
Languages written with the Latin alphabet
Page last modified: 07.11.24
[top]
You can support this site by Buying Me A Coffee, and if you like what you see on this page, you can use the buttons below to share it with people you know.

If you like this site and find it useful, you can support it by making a donation via PayPal or Patreon, or by contributing in other ways. Omniglot is how I make my living.
Note: all links on this site to Amazon.com, Amazon.co.uk
and Amazon.fr
are affiliate links. This means I earn a commission if you click on any of them and buy something. So by clicking on these links you can help to support this site.
[top]